Ottoman Empire
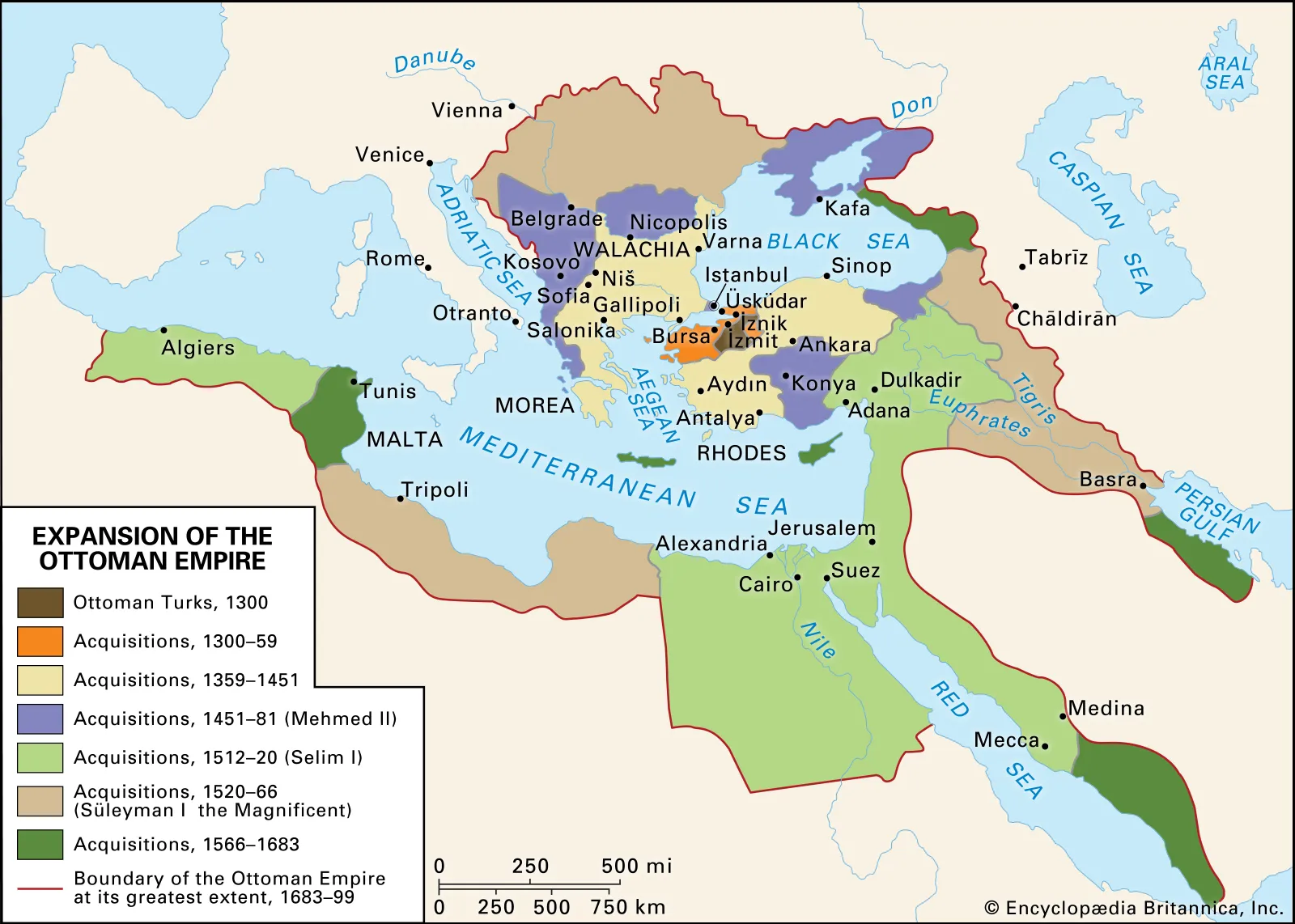
Ottoman Empire, empire created by Turkish tribes in Anatolia (Asia Minor) that grew to be one of the most powerful states in the world during the 15th and 16th centuries. The Ottoman period spanned more than 600 years and came to an end only in 1922, when it was replaced by the Turkish Republic and various successor states in southeastern Europe and the Middle East. At its height the empire encompassed most of southeastern Europe to the gates of Vienna, including present-day Hungary, the Balkan region, Greece, and parts of Ukraine; portions of the Middle East now occupied by Iraq, Syria, Israel, and Egypt; North Africa as far west as Algeria; and large parts of the Arabian Peninsula. The term Ottoman is a dynastic appellation derived from Osman I (Arabic: ʿUthmān), the nomadic Turkmen chief who founded both the dynasty and the empire about 1300.
The Ottoman State To 1481: The Age Of Expansion
The first period of Ottoman history was characterized by almost continuous territorial expansion, during which Ottoman dominion spread out from a small northwestern Anatolian principality to cover most of southeastern Europe and Anatolia. The political, economic, and social institutions of the classical Islamic empires were amalgamated with those inherited from Byzantium and the great Turkish empires of Central Asia and were reestablished in new forms that were to characterize the area into modern times.
Origins and expansion of the Ottoman state, c. 1300–1402
In their initial stages of expansion, the Ottomans were leaders of the Turkish warriors for the faith of Islam, known by the honorific title ghāzī (Arabic: “raider”), who fought against the shrinking Christian Byzantine state. The ancestors of Osman I, the founder of the dynasty, were members of the Kayı tribe who had entered Anatolia along with a mass of Turkmen Oğuz nomads. Those nomads, migrating from Central Asia, established themselves as the Seljuq dynasty in Iran and Mesopotamia in the mid-11th century, overwhelmed Byzantium after the Battle of Manzikert (1071), and occupied eastern and central Anatolia during the 12th century. The ghazis fought against the Byzantines and then the Mongols, who invaded Anatolia following the establishment of the Il-Khanid (Ilhanid) empire in Iran and Mesopotamia in the last half of the 13th century. With the disintegration of Seljuq power and its replacement by Mongol suzerainty, enforced by direct military occupation of much of eastern Anatolia, independent Turkmen principalities—one of which was led by Osman—emerged in the remainder of Anatolia.
Osman and Orhan
Following the final Mongol defeat of the Seljuqs in 1293, Osman emerged as prince (bey) of the border principality that took over Byzantine Bithynia in northwestern Anatolia around Bursa, commanding the ghazis against the Byzantines in that area. Hemmed in on the east by the more powerful Turkmen principality of Germiyan, Osman and his immediate successors concentrated their attacks on Byzantine territories bordering the Bosporus and the Sea of Marmara to the west. The Ottomans, left as the major Muslim rivals of Byzantium, attracted masses of nomads and urban unemployed who were roaming through the Middle East searching for means to gain their livelihoods and seeking to fulfill their religious desire to expand the territory of Islam. The Ottomans were able to take advantage of the decay of the Byzantine frontier defense system and the rise of economic, religious, and social discontent in the Byzantine Empire and, beginning under Osman and continuing under his successors Orhan (Orkhan, ruled 1324–60) and Murad I (1360–89), took over Byzantine territories, first in western Anatolia and then in southeastern Europe. It was only under Bayezid I (1389–1402) that the wealth and power gained by that initial expansion were used to assimilate the Anatolian Turkish principalities to the east.
By 1300 Osman ruled an area in Anatolia stretching from Eskişehir (Dorylaeum) to the plains of İznik (Nicaea), having defeated several organized Byzantine efforts to curb his expansion. Byzantine attempts to secure Il-Khanid support against the Ottomans from the east were unsuccessful, and the Byzantine emperor’s use of mercenary troops from western Europe caused more damage to his own territory than to that of the Turks. The Ottomans lacked effective siege equipment, however, and were unable to take the major cities of Bithynia. Nor could they move against their increasingly powerful Turkmen neighbours, the Aydın and Karası dynasties, which had taken over Byzantine territory in southwestern Anatolia. Orhan’s capture of Bursa in 1324 (some sources date the event to 1326) provided the first means for developing the administrative, economic, and military power necessary to make the principality into a real state and to create an army. Orhan began the military policy, expanded by his successors, of employing Christian mercenary troops, thus lessening his dependence on the nomads.
Orhan soon was able to capture the remaining Byzantine towns in northwestern Anatolia: İznik (1331), İzmit (1337), and Üsküdar (1338). He then moved against his major Turkmen neighbours to the south. Taking advantage of internal conflicts, Orhan annexed Karası in 1345 and gained control of the area between the Gulf of Edremit and Kapıdağı (Cyzicus), reaching the Sea of Marmara. He thus put himself in a position to end the lucrative monopoly enjoyed by the city of Aydın, that of providing mercenary troops to competing Byzantine factions in Thrace and at the Byzantine capital, Constantinople (present-day Istanbul). The expansion also enabled the Ottomans to replace Aydın as the principal ally of the Byzantine emperor John VI Cantacuzenus. The consequent entry of Ottoman troops into Europe gave them a direct opportunity to see the possibilities for conquest offered by Byzantine decadence. The collapse of Aydın following the death of its ruler, Umur Bey, left the Ottomans alone as the leaders of the ghazis against the Byzantines. Orhan helped Cantacuzenus take the throne of Byzantium from John V Palaeologus and as a reward secured the right to ravage Thrace and to marry the emperor’s daughter Theodora.
Ottoman raiding parties began to move regularly through Gallipoli into Thrace. Huge quantities of captured booty strengthened Ottoman power and attracted thousands from the uprooted Turkmen masses of Anatolia into Ottoman service. Starting in 1354, Orhan’s son Süleyman transformed Gallipoli, a peninsula on the European side of the Dardanelles, into a permanent base for expansion into Europe and refused to leave, despite the protests of Cantacuzenus and others. From Gallipoli Süleyman’s bands moved up the Maritsa River into southeastern Europe, raiding as far as Adrianople. Cantacuzenus soon fell from power, at least partially because of his cooperation with the Turks, and Europe began to be aware of the extent of the Turkish danger